The ability to innovate is one of the most important drivers of success in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape. For companies to stay competitive, they must be able to create new and improved products that meet the changing needs of consumers. One of the key factors that enable successful product innovation is organizational creativity. Organizational creativity refers to the collective ability of an organization to generate novel ideas, solutions, or products. It is a critical component in fostering an environment where innovation can thrive. This study aims to analyze organizational creativity as a central element in the process of product innovation by examining various management models that encourage and nurture creativity within organizations.
In the following sections, we will explore the concept of organizational creativity, its role in product innovation, and how different management models can either support or hinder the creative process. We will also highlight real-world examples of organizations that have successfully leveraged creativity to drive product innovation, and provide recommendations for managers looking to cultivate a more innovative culture within their own organizations.
Defining Organizational Creativity
Organizational creativity is the ability of an organization to foster and facilitate the generation of novel and useful ideas by its members. It is a process that involves the creative contributions of individuals, teams, and organizational systems working together to solve problems, explore new opportunities, and create value. Unlike individual creativity, which focuses on the creative potential of a single person, organizational creativity is the collective effort that relies on collaboration, knowledge sharing, and an environment that supports innovation.
Several factors contribute to organizational creativity, including:
- Individual creativity: The ideas and contributions of individual employees play a crucial role in generating innovative solutions.
- Team collaboration: Teams often bring together diverse perspectives, skills, and expertise that can lead to more creative solutions than individual efforts alone.
- Organizational culture: An organization’s culture shapes the way employees approach problem-solving and innovation. A culture that values creativity, risk-taking, and open communication will be more likely to foster creativity.
- Leadership and management: Leaders who encourage creativity, provide resources, and create a safe environment for experimentation can help stimulate innovative thinking.
- Organizational structure: A flexible structure that allows for the free flow of ideas, minimal bureaucracy, and cross-functional collaboration can facilitate the creative process.
The Role of Organizational Creativity in Product Innovation
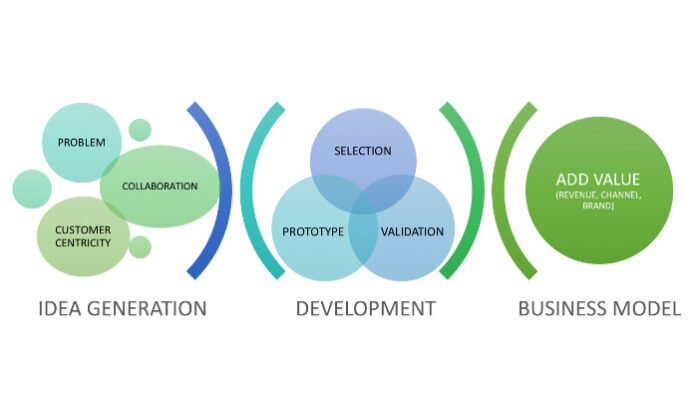
Product innovation is the process of developing new or improved products that offer value to consumers. It involves identifying customer needs, generating ideas, designing prototypes, testing, and launching products into the market. Creativity plays a central role throughout the product innovation process, as it enables organizations to come up with unique ideas and solutions that differentiate them from competitors.
Stages of Product Innovation
- Idea Generation: The first stage of product innovation involves generating ideas that can address an unmet need or improve an existing product. Creativity is essential at this stage, as the most innovative solutions often come from thinking outside the box or combining ideas from different fields. This is where organizational creativity can have the most impact. When teams of individuals with diverse backgrounds and expertise collaborate, they are more likely to generate novel ideas that are not bound by conventional thinking.
- Concept Development and Design: After the initial idea generation, the next step is to develop the concept and design the product. Creativity is still essential during this phase, as product teams must come up with unique ways to make the concept feasible and appealing to consumers. This stage requires creative problem-solving skills to address technical challenges, improve product features, and optimize user experience.
- Prototyping and Testing: Once a product concept is developed, it is often turned into a prototype for testing and refinement. Creativity is important during this stage because prototypes frequently require iterative design and modification. Creativity allows teams to address unforeseen issues, refine features, and find new ways to improve the product before it is launched to the market.
- Commercialization: The final stage of product innovation involves bringing the product to market. Organizational creativity continues to be important here, as the company must develop marketing strategies, sales channels, and distribution plans that align with the product’s unique value proposition. Creativity in packaging, branding, and customer experience can make a significant difference in the product’s success.
Examples of Organizational Creativity in Product Innovation
- Apple: Apple is a prime example of how organizational creativity drives product innovation. From the iPod to the iPhone, Apple has consistently introduced groundbreaking products that have transformed entire industries. Apple’s success can be attributed to its strong organizational culture, which prioritizes creativity, collaboration, and a commitment to designing products that offer exceptional user experiences. The company’s leadership, particularly Steve Jobs, played a pivotal role in creating a culture of innovation that encouraged employees to think creatively and push the boundaries of what was possible.
- Tesla: Tesla is another example of a company that has leveraged organizational creativity to drive product innovation. Through its electric vehicles and energy solutions, Tesla has disrupted the automotive and energy industries. Tesla’s organizational creativity can be seen in its commitment to solving complex problems like battery technology, vehicle design, and sustainability. The company fosters creativity by allowing teams to experiment with new ideas and approaches, often taking risks that traditional companies might avoid.
- Google: Google has become known for its innovation in both products and services, ranging from the Google search engine to Android and Google Maps. Google’s creativity stems from its open and collaborative culture, where employees are encouraged to share ideas and work across functions. The company’s management model includes allowing employees to spend a portion of their time on personal creative projects, leading to innovations like Gmail and Google News.
Management Models That Encourage Organizational Creativity
While organizational creativity is influenced by several factors, one of the most important is the management model in place within the company. The management model defines how resources, people, and ideas are organized, how decisions are made, and how innovation is encouraged. The following management models are particularly effective in fostering creativity and innovation within organizations:
1. The Open Innovation Model
The open innovation model encourages organizations to look outside their own boundaries for ideas and solutions. This model emphasizes collaboration with external partners, including customers, suppliers, and even competitors. By fostering an open exchange of ideas and knowledge, companies can tap into a wider pool of creativity, leading to more innovative products and services. For example, companies may collaborate with academic institutions or startups to develop new technologies or explore novel product concepts.
2. The Agile Management Model
Agile management focuses on flexibility, iterative development, and collaboration. The Agile model allows organizations to respond quickly to changes in the market or customer demands, making it ideal for product innovation. Teams work in short cycles (or “sprints”) to develop product features or solve problems, with regular feedback and adjustments. This model encourages creativity by promoting experimentation, rapid prototyping, and continuous improvement.
3. The Design Thinking Model
Design thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that prioritizes empathy, ideation, and prototyping. This model encourages organizations to deeply understand the needs and experiences of their customers and to generate creative solutions that address these needs. The design thinking process involves defining the problem, ideating solutions, creating prototypes, and testing them with users. It is a highly creative and iterative process that places a strong emphasis on collaboration and user feedback.
4. The Holacracy Model
Holacracy is a management model that decentralizes decision-making and distributes authority across the organization. In a holacracy, employees are given autonomy to make decisions within their areas of expertise, which fosters a culture of innovation and creativity. By giving employees more control over their work, this model encourages them to take ownership of creative processes and to contribute ideas that can lead to new products or improvements.
Overcoming Challenges to Organizational Creativity
Despite its importance, fostering creativity within an organization can be challenging. Several barriers may inhibit creativity, including rigid organizational structures, lack of resources, fear of failure, and resistance to change. To overcome these challenges, organizations must actively cultivate a culture that supports creativity and innovation. This may involve:
- Providing resources for experimentation: Organizations should invest in the tools, technology, and training necessary for employees to experiment and test new ideas.
- Encouraging risk-taking: Fear of failure can stifle creativity. Leaders should create a safe environment where employees are encouraged to take risks and learn from mistakes.
- Promoting cross-functional collaboration: Innovation often arises from diverse perspectives. Organizations should foster collaboration between departments and encourage employees from different functions to work together on creative projects.
- Recognizing and rewarding creativity: Employees should be acknowledged and rewarded for their creative contributions. This reinforces the importance of creativity and motivates others to think creatively.
Conclusion
In this study, we have analyzed organizational creativity as a key element in the process of product innovation. Creativity is essential at every stage of product development, from idea generation to commercialization. By fostering an environment that supports creativity, organizations can drive product innovation and gain a competitive advantage. Different management models, such as open innovation, agile management, design thinking, and holacracy, can play a significant role in encouraging organizational creativity. However, organizations must also address the challenges that hinder creativity, such as fear of failure and rigid structures, to create a culture of innovation. Ultimately, organizations that prioritize creativity and provide the necessary resources and support are more likely to succeed in developing groundbreaking products that meet the evolving needs of consumers.